
اگر به یک وب سایت یا فروشگاه رایگان با فضای نامحدود و امکانات فراوان نیاز دارید بی درنگ دکمه زیر را کلیک نمایید.
ایجاد وب سایت یادسته بندی سایت
محبوب ترین ها
پرفروش ترین ها
پر فروش ترین های فورکیا
 دانلود فایلهای بسته آمادهچاپ و نصب تابلو اعلانات مسجدنما هفته پنجم فروردین ماه 1403
دانلود فایلهای بسته آمادهچاپ و نصب تابلو اعلانات مسجدنما هفته پنجم فروردین ماه 1403 دانلود فایلهای بسته آمادهچاپ و نصب تابلو اعلانات مسجدنما هفته اول اردیبهشت ماه 1403
دانلود فایلهای بسته آمادهچاپ و نصب تابلو اعلانات مسجدنما هفته اول اردیبهشت ماه 1403 دانلود فایلهای بسته آمادهچاپ و نصب تابلو اعلانات مسجدنما هفته دوم فروردین ماه 1403
دانلود فایلهای بسته آمادهچاپ و نصب تابلو اعلانات مسجدنما هفته دوم فروردین ماه 1403 دانلود فایلهای بسته آمادهچاپ و نصب تابلو اعلانات مسجدنما فروردین ماه 1403
دانلود فایلهای بسته آمادهچاپ و نصب تابلو اعلانات مسجدنما فروردین ماه 1403 فایل نقشه ی تابلو فرش دستباف طرح طبیعت کلبه زیبا
فایل نقشه ی تابلو فرش دستباف طرح طبیعت کلبه زیبا دانلود فایلهای بسته آمادهچاپ و نصب تابلو اعلانات مسجدنما هفته سوم فروردین ماه 1403
دانلود فایلهای بسته آمادهچاپ و نصب تابلو اعلانات مسجدنما هفته سوم فروردین ماه 1403 برنامه اکسل متره و برآورد،تهیه صورت وضعیت راه و باند سال1403
برنامه اکسل متره و برآورد،تهیه صورت وضعیت راه و باند سال1403 دانلود بسته 8000 تست-عمومی، اختصاصی،تخصصی-استخدامی آموزش پرورش
دانلود بسته 8000 تست-عمومی، اختصاصی،تخصصی-استخدامی آموزش پرورش پاسخنامه کتاب Introductory Steps to Understanding
پاسخنامه کتاب Introductory Steps to Understanding دانلود رایگان کتاب صوتی از سکس تا فراآگاهی
دانلود رایگان کتاب صوتی از سکس تا فراآگاهی دانلود کتاب صوتی روانشناسی تصویر ذهنی ماکسول مالتز
دانلود کتاب صوتی روانشناسی تصویر ذهنی ماکسول مالتز![دانلود پاورپوینت در مورد [سلول های بنیادی] - شامل 4 فایل مختلف - قابل ویرایش و ارائه - ppt](https://4kia.ir/s4/img_project/22638_1661011327.jpg) دانلود پاورپوینت در مورد [سلول های بنیادی] - شامل 4 فایل مختلف - قابل ویرایش و ارائه - ppt
دانلود پاورپوینت در مورد [سلول های بنیادی] - شامل 4 فایل مختلف - قابل ویرایش و ارائه - ppt پاورپوینت بازی زندگی است درس 17 تفکر و سواد رسانه ای دهم
پاورپوینت بازی زندگی است درس 17 تفکر و سواد رسانه ای دهم پاورپوینت بز یا سگ تفکر و سبک زندگی هفتم
پاورپوینت بز یا سگ تفکر و سبک زندگی هفتم دانلود جزوه امور مالی و حقوق ثبتی در دفاتر اسناد رسمی
دانلود جزوه امور مالی و حقوق ثبتی در دفاتر اسناد رسمی![دانلود حل المسائل [طراحی و تحلیل آزمایش]: ویرایش هشتم - داگلاس مونتگومری ( 8 ) - زبان انگلیسی - pdf](https://4kia.ir/s4/img_project/22638_1659774456.jpg) دانلود حل المسائل [طراحی و تحلیل آزمایش]: ویرایش هشتم - داگلاس مونتگومری ( 8 ) - زبان انگلیسی - pdf
دانلود حل المسائل [طراحی و تحلیل آزمایش]: ویرایش هشتم - داگلاس مونتگومری ( 8 ) - زبان انگلیسی - pdf دانلود پاورپوینت چیستی انسان 2 درس 10 فلسفه یازدهم انسانی
دانلود پاورپوینت چیستی انسان 2 درس 10 فلسفه یازدهم انسانی دانلود 3 بک دراپ کودک تم فوتبال-کد 8082-8080
دانلود 3 بک دراپ کودک تم فوتبال-کد 8082-8080 پاورپوینت ادبیات بومی 2 درس آزاد فارسی دوازدهم
پاورپوینت ادبیات بومی 2 درس آزاد فارسی دوازدهم پاورپوینت درس 2 علوم تجربی پایه چهارم دبستان (ابتدایی): مخلوط ها در زندگی
پاورپوینت درس 2 علوم تجربی پایه چهارم دبستان (ابتدایی): مخلوط ها در زندگی بسته آموزشی ماساژ کاریز خانواده
بسته آموزشی ماساژ کاریز خانواده مجموعه اسکیس معماری از بناهای ایرانی
مجموعه اسکیس معماری از بناهای ایرانی پاورپوینت درس دهم قرآن هشتم سوره یس، سوره صافات و تفسیر نمونه
پاورپوینت درس دهم قرآن هشتم سوره یس، سوره صافات و تفسیر نمونه دانلود رایگان کتاب صوتی روش ها و فنون مشاوره دکتر عبدالله شفیع آبادی
دانلود رایگان کتاب صوتی روش ها و فنون مشاوره دکتر عبدالله شفیع آبادی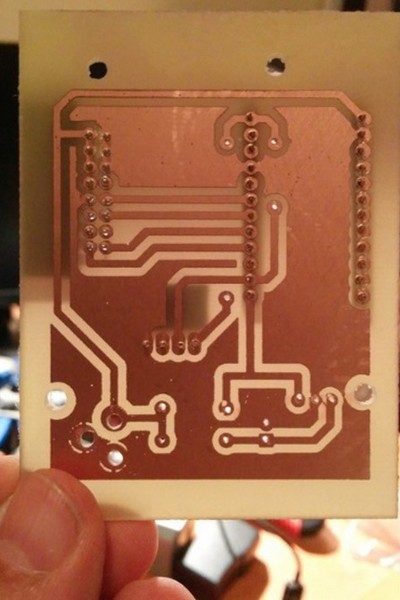 آموزش نحوه تهیه مدار چاپی
آموزش نحوه تهیه مدار چاپی دانلود پاورپوینت فصل هفتم ریاضی پنجم آمار و احتمال همراه با پاسخ فعالیت ها و تمارین
دانلود پاورپوینت فصل هفتم ریاضی پنجم آمار و احتمال همراه با پاسخ فعالیت ها و تمارین پاورپوینت پدافند غیرعامل درس 10 آمادگی دفاعی نهم
پاورپوینت پدافند غیرعامل درس 10 آمادگی دفاعی نهم دانلود کتاب صوتی روح تسخیر ناپذیر(سفر به ماورای وجود) مایکل سینگر
دانلود کتاب صوتی روح تسخیر ناپذیر(سفر به ماورای وجود) مایکل سینگر Electric Vehicle Components and Charging Technologies: Design, modeling, simulation and control (Transportation)
Electric Vehicle Components and Charging Technologies: Design, modeling, simulation and control (Transportation) Heating Systems: Design, Applications and Technology
Heating Systems: Design, Applications and Technologyپر بازدید ترین های فورکیا
 فروش فیلتر بورسی استریکلی فقط 75 هزار تومان
فروش فیلتر بورسی استریکلی فقط 75 هزار تومان کسب درآمد اینترنتی 300000 تومان در خانه در کمتر از 30 دقیقه
کسب درآمد اینترنتی 300000 تومان در خانه در کمتر از 30 دقیقه کسب و کار اینترنتی با درآمد میلیونی
کسب و کار اینترنتی با درآمد میلیونی كسب درآمد اينترنتي روزانه حداقل100هزار تومان تضميني
كسب درآمد اينترنتي روزانه حداقل100هزار تومان تضميني کسب درآمد ابدی و بی نهایت 100% واقعی
کسب درآمد ابدی و بی نهایت 100% واقعی کسب درآمد روزانه حداقل یک میلیون تومان ! کاملا حلال و واقعـی !!
کسب درآمد روزانه حداقل یک میلیون تومان ! کاملا حلال و واقعـی !! مجموعه ی آموزش تعمیر لامپ کم مصرف (از مبتدی تا پیشرفته)
مجموعه ی آموزش تعمیر لامپ کم مصرف (از مبتدی تا پیشرفته) دانلود پکیج درآمدزایی 400هزارتومن در 40دقیقه (مخصوص شرایط تورم 50 درصدی)
دانلود پکیج درآمدزایی 400هزارتومن در 40دقیقه (مخصوص شرایط تورم 50 درصدی) آموزش بازكردن انواع قفل ها بدون كليد(ويژه)
آموزش بازكردن انواع قفل ها بدون كليد(ويژه) کسب و کار اینترنتی در منزل
کسب و کار اینترنتی در منزل آموزش برنامه نویسی آردوینو
آموزش برنامه نویسی آردوینو دانلود مجموعه آموزشی پایپینگ ( Piping ) و نقشه خوانی + آموزش سه نرم افزار طراحی و تحلیل لوله کشی صنعتی
دانلود مجموعه آموزشی پایپینگ ( Piping ) و نقشه خوانی + آموزش سه نرم افزار طراحی و تحلیل لوله کشی صنعتی بازگردانی پیامک های حذف شده- ریکاوری پیامک ۱۰۰٪ عملی
بازگردانی پیامک های حذف شده- ریکاوری پیامک ۱۰۰٪ عملی آموزش رایگان کسب درآمد از سایت الیمپ ترید ( olymp trade )
آموزش رایگان کسب درآمد از سایت الیمپ ترید ( olymp trade ) اموزش ویرایش امضا و پکیج برنامه اندروید و کسب درامد از مارکت های اندرویدی
اموزش ویرایش امضا و پکیج برنامه اندروید و کسب درامد از مارکت های اندرویدی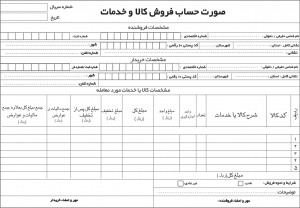 دانلود نمونه فاکتور آماده با فرمت ورد - اکسل و عکس
دانلود نمونه فاکتور آماده با فرمت ورد - اکسل و عکس آموزش ساخت بازی بدون دانش برنامه نویسی و طراحی سه بعدی مبتدی تا پیشرفته با نرم افزار
آموزش ساخت بازی بدون دانش برنامه نویسی و طراحی سه بعدی مبتدی تا پیشرفته با نرم افزار آموزش كامل تعمير لامپ كم مصرف(اختصاصي)
آموزش كامل تعمير لامپ كم مصرف(اختصاصي) اموزش کسب درامد از اینترنت روزانه ۳میلیون تومان تضمینی و تست شده
اموزش کسب درامد از اینترنت روزانه ۳میلیون تومان تضمینی و تست شده نسخه خطی اشعار و پیشگویی های شاه نعمت الله ولی
نسخه خطی اشعار و پیشگویی های شاه نعمت الله ولی درامدزایی در خواب! (تعجب نکنید! بخوانید)
درامدزایی در خواب! (تعجب نکنید! بخوانید) مدار داخلی واکی تاکی(اموزش ساخت)
مدار داخلی واکی تاکی(اموزش ساخت) کتاب افزایش ممبر کانال تلگرام
کتاب افزایش ممبر کانال تلگرام اندیکاتور ای کیو آپشن
اندیکاتور ای کیو آپشن دانلود100% رایگان نرم افزار تبلیغات در تلگرام + آموزش کامل و فیلم آموزشی
دانلود100% رایگان نرم افزار تبلیغات در تلگرام + آموزش کامل و فیلم آموزشی روش اصلی موفقیت در کنکور و آزمون ها(پزشکی، حقوق، مهندسی، نمونه و تیزهوشان) با پکیج کنکورپلاس
روش اصلی موفقیت در کنکور و آزمون ها(پزشکی، حقوق، مهندسی، نمونه و تیزهوشان) با پکیج کنکورپلاس مجموعه آزمایشات و گزارشات روانشناسی تجربی (شامل شرح 36 آزمایش) کاملترین مجموعه در اینترنت
مجموعه آزمایشات و گزارشات روانشناسی تجربی (شامل شرح 36 آزمایش) کاملترین مجموعه در اینترنت چگونه هر شخصی را عاشق خود کنیم ارزان
چگونه هر شخصی را عاشق خود کنیم ارزانبرچسب های مهم
پیوند ها
محبوبيت جهاني مکمل هاي گياهي و وعده هايي که در درمان بيماري هاي مختلف بيماري دارند، موجب علاقه بي سابقه اي به درک مبناي مولکولي فعاليت بيولوژيکي داروهاي سنتي شده است. پزشکی گیاهی: جنبه های بیولوژیکی و بالینی بر ارائه شواهد علمی کنونی اثرات بیوما مولکولی گیاهان انتخاب شده و ارتباط آنها با نتیجه بالینی و ارتقاء سلامت انسان است. این شامل روش های تجربی برای بررسی اجزای فعال زیستی در گیاهان است. این کتاب همچنین به چالش های اخلاقی استفاده از داروهای گیاهی و ادغام آن با طب مدرن و مبتنی بر شواهد اشاره دارد.
این اثر از کار کارشناسان پیشرو بین المللی در حوزه های مختلف، شامل یک بررسی عمیق علمی از اثرات گیاهان فردی و همچنین استفاده از آنها در درمان بیماری های مهم مانند سرطان، بیماری های قلبی عروقی، اختلالات پوستی، بیماری های نوروژنیک و دیابت. با توجه به ارتباطات قوی بین استرس اکسیداتیو، پیری و بیماری، خواص آنتی اکسیدانی قوی گیاهان و ادویه ها نیز مورد بررسی قرار می گیرند. گیاهان برجسته برخی از داروهای به طور گسترده استفاده می شود و دامنه گسترده ای از جمله گیاهان گلدار، میوه ها و انواع توت ها، ریشه ها و ریزوم ها و قارچ ها را پوشش می دهد.
واقعیت این است که ترکیب محصولات طبیعی می تواند بسیار متفاوت باشد و آلودگی و شناسایی اشتباه رخ دهد، مسائل مهم در استفاده از داروهای گیاهی است. استفاده از طیف سنج جرمی و تکنیک شمارش انگشت شمسی به عنوان وسیله ای برای شناسایی و تأیید صحت گیاهان، به منظور کمک به ایجاد یک سطح کنترل کیفیت جدید برای تولید عصاره های گیاهی است.
به عنوان نیاز به ارتقاء و مقابله با مقرون به صرفه، به خصوص در جمعیت رو به رشد، نیازمند بررسی دقیق علمی داروهای گیاهی است. این حجم به موقع و جامع این نیاز را مورد توجه قرار می دهد و یک متن مهم برای متخصصان و پژوهشگران پزشکی و نیز کسانی است که علاقه مند به داروهای گیاهی یا مکمل هستند
لینک سایت اصلی جهت اطلاعات بیشتر
Series Preface During evolution, oxygen—itself a free radical—was chosen as the terminal electron acceptor for respiration; hence, the formation of oxygen-derived
free radicals is a consequence of aerobic metabolism. These oxygen-derived radicals are involved in oxidative damage to cell components inherent in several pathophysiological situations. Conversely, cells convene antioxidant mecha- nisms to counteract the effects of oxidants in either a highly specific manner (e.g., by superoxide dismutases) or a less-specific manner (e.g., through small molecules such as glutathione, vitamin E, and vitamin C). Oxidative stress, as defined classically, entails an imbalance between oxidants and antioxidants. However, the same free radicals that are generated during oxidative stress are pro- duced during normal metabolism and, as a corollary, are involved in both human health and disease by virtue of their involvement in the regulation of signal transduction and gene expression, activa- tion of receptors and nuclear transcription factors, antimicrobial and cytotoxic actions of immune system cells, and aging and age-related degenerative diseases. In recent years, research disciplines focusing on oxidative stress have increased our knowledge of the importance of the cell redox status and the recognition of oxidative stress as a process with implications for many pathophysiological states. From this multi- and interdisciplinary interest in oxidative stress emerges a concept that attests the vast consequences of the complex and dynamic interplay of oxidants and antioxidants in cellular and tissue settings. Consequently, our view of oxidative stress is both growing in scope and following new directions. Likewise, the term “reactive oxygen species,” adopted at some stage to highlight nonradical/radical oxidants, now fails to reflect the rich variety of other species in free-radical biology and medicine, encompassing nitrogen-, sulfur-, oxygen-, and carbon-centered radicals. These reactive species are involved in the redox regulation of cell functions and, as a corollary, oxidative stress is increasingly viewed as a major upstream component in cell-signaling cascades involved in inflammatory responses, stimulation of cell adhesion molecules, and chemoattractant production and as an early component of age-related neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and Huntington’s diseases, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Hydrogen peroxide is probably the most important redox-signaling molecule that, among others, can activate nuclear factor κB (NF-κB), NF-E2 related factor 2 (Nrf2), and other universal transcription factors, and that is involved in the redox regulation of insulin and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling. These pleiotropic effects of hydrogen peroxide are largely accounted for by changes in the thiol/disulfide status of a cell, an important determi- nant of the cell’s redox status with clear involvement in adaptation, proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and necrosis. The identification of oxidants in the regulation of redox cell signaling and gene expression is a significant breakthrough in the field of oxidative stress. The classical definition of oxidative stress as an imbalance between the production of oxidants and the occurrence of antioxidant defenses now seems to provide a limited depiction of oxidative stress, although it emphasizes the significance of cell redox status. Because individual signaling and control events occur through discrete redox pathways rather than through global balances, a new definition of oxidative stress was advanced by Dean P. Jones as a disruption of redox signaling and control that recognizes the occurrence of compartmentalized cellular redox circuits. These concepts are anticipated to serve as platforms for the development of tissue-specific therapeutics tailored to discrete, compartmentalized redox circuits. This, in essence, dictates the principles of drug development–guided knowledge of the mechanisms of oxidative stress. Hence, successful interventions will take advantage of new knowl- edge of compartmentalized redox control and free-radical scavenging.
Contents
Series Preface....................................................................................................................................ix Foreword ...........................................................................................................................................xi Preface............................................................................................................................................ xiii Editors..............................................................................................................................................xv Contributors ...................................................................................................................................xvii
Chapter 1 Herbal Medicine: An Introduction to Its History, Usage,
Regulation, Current Trends, and Research Needs .......................................................1 Sissi Wachtel-Galor and Iris F. F. Benzie
Chapter 2 Antioxidants in Herbs and Spices: Roles in Oxidative Stress
and Redox Signaling .................................................................................................. 11
Ingvild Paur, Monica H. Carlsen, Bente Lise Halvorsen, and Rune Blomhoff
Chapter 3 Evaluation of the Nutritional and Metabolic Effects of Aloe vera.............................37
Meika Foster, Duncan Hunter, and Samir Samman
Chapter 4 Bilberry (Vaccinium myrtillus L.) .............................................................................. 55
Wing-kwan Chu,Sabrina C. M. Cheung, Roxanna A. W. Lau, and Iris F. F. Benzie
Chapter 5 Cordyceps as an Herbal Drug ....................................................................................73
Bao-qin Lin and Shao-ping Li
Chapter 6 Cranberry ................................................................................................................. 107
Catherine C. Neto and Joe A. Vinson
Chapter 7 The Amazing and Mighty Ginger............................................................................ 131
Ann M. Bode and Zigang Dong
Chapter 8 Biological Activities of Ginseng and Its Application to Human Health .................. 157
Jae Joon Wee, Kyeong Mee Park, and An-Sik Chung
Chapter 9 Ganoderma lucidum (Lingzhi or Reishi): A Medicinal Mushroom........................ 175
Sissi Wachtel-Galor, John Yuen, John A. Buswell, and Iris F. F. Benzie
Chapter 10 Pomegranate Ellagitannins ...................................................................................... 201
David Heber
Chapter 11 Medical Attributes of St. John’s Wort (Hypericum perforatum).............................. 211
Kenneth M. Klemow, Andrew Bartlow, Justin Crawford,
Neil Kocher, Jay Shah, and Michael Ritsick
Chapter 12 Health Benefits of Tea .............................................................................................. 239
Mauro Serafini, Daniele Del Rio, Yao Denis N’Dri,
Saverio Bettuzzi, and Ilaria Peluso
Chapter 13 Turmeric, the Golden Spice: From Traditional Medicine to Modern Medicine ......263
Sahdeo Prasad and Bharat B. Aggarwal
Chapter 14 Biomolecular and Clinical Aspects of Chinese Wolfberry .....................................289
Peter Bucheli, Qiutao Gao, Robert Redgwell, Karine Vidal,
Junkuan Wang, and Weiguo Zhang
Chapter 15 Botanical Phenolics and Neurodegeneration ........................................................... 315
Albert Y. Sun, Qun Wang, Agnes Simonyi, and Grace Y. Sun
Chapter 16 Cardiovascular Disease ............................................................................................ 333
Richard Walden and Brian Tomlinson
Chapter 17 Herbs and Spices in Cancer Prevention and Treatment ........................................... 361
Christine M. Kaefer and John A. Milner
Chapter 18 Herbal Treatment for Dermatologic Disorders......................................................... 383
Philip D. Shenefelt
Chapter 19 Diabetes and Herbal (Botanical) Medicine..............................................................405
William T. Cefalu, Jaqueline M. Stephens, and David M. Ribnicky
Chapter 20 Bioactive Components in Herbal Medicine: Experimental Approaches ................. 419
Foo-tim Chau, Kwok-pui Fung, Chi-man Koon, Kit-man Lau, Shui-yin
Wei, and Ping-chung Leung
Chapter 21 Ethics of Using Herbal Medicine as Primary or Adjunct Treatment
and Issues of Drug–Herb Interaction ....................................................................... 439 Lauren Girard and Sunita Vohra
Chapter 22 Integration of Herbal Medicine into Evidence-Based Clinical Practice:
Current Status and Issues ......................................................................................... 453 Anthony Lin Zhang, Charlie Changli Xue, and Harry H. S. Fong
مبلغ قابل پرداخت 21,556 تومان
برچسب های مهم